- Declaring Variables in PHP
- PHP Data Types
- PHP Arrays
- Types of PHP Operators
- PHP Strings
- PHP Expressions
- PHP Control Structures
- PHP Functions
- PHP Form Handling – Read Form Inputs & Handle File Uploads
- How to Connect PHP to MySQL Database Using MySQLi
- Executing Simple Queries in PHP
- Handling Results in PHP
- Handling Sessions and Cookies
Introduction to PHP
PHP stands for PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor. It is a free and popular scripting language used mainly for making websites interactive. You write PHP code inside HTML pages, and when a user visits your page, the server runs the PHP code and sends back the result as a web page.
PHP is great for making websites that change based on user actions — like forms, logins, or displaying data from a database.
Key Features of PHP
- Free and works on Windows, Linux, and Mac computers.
- Works with popular web servers like Apache and Nginx.
- Can create dynamic content that changes as users interact.
- Can connect to databases like MySQL to store or get information.
- Can handle file operations (create, read, update, delete files).
- Can read data from web forms like text boxes and buttons.
- Manages sessions and cookies to remember users.
- Supports security features like encryption and access control.
- PHP files end with
.phpand can have HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and PHP code together.
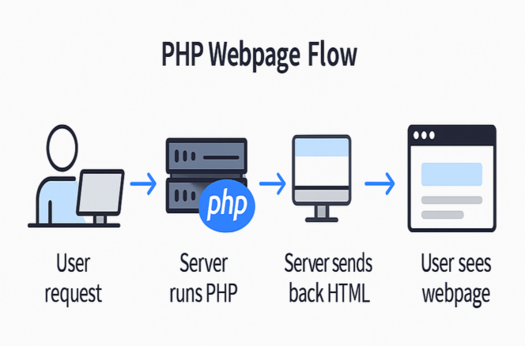
How PHP Works
- User opens a website or submits a form.
- Server checks if PHP code needs to run.
- PHP code runs on the server.
- If needed, PHP talks to a database to get or save data.
- Server sends back a webpage with HTML to the user.
This makes websites smart and personal for every user.
Basic PHP Syntax
PHP code is put between <?php and ?> tags inside an HTML file. Every PHP command ends with a semicolon ;.
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<?php
echo "Hello, this is my first PHP script!";
?>
</body>
</html>
Output:
Hello, this is my first PHP script!
PHP Comments
Comments help explain your code. PHP ignores comments when running the script.
Types of comments:
- Single line: starts with
//or# - Multi-line: between
/*and*/
Example:
<?php
// This is a single-line comment
# This is also a single-line comment
/*
This is a
multi-line comment
*/
echo "Comments in PHP!";
?>
Case Sensitivity in PHP
- Keywords and function names are not case-sensitive.
- Variable names are case-sensitive.
Example:
<?php
$color = "red";
echo "Car color: " . $color . "<br>";
echo "House color: " . $COLOR . "<br>";
?>
Output:
Car color: red
House color:
Reading Data from Web Forms
You can collect user input using $_GET or $_POST in PHP.
HTML Form Example:
<form method="post" action="process.php">
Name: <input type="text" name="username"><br>
Gender:
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="Male"> Male
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="Female"> Female<br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
PHP to handle form data:
<?php
$username = $_POST['username'];
$gender = $_POST['gender'];
echo "Name: " . $username . "<br>";
echo "Gender: " . $gender;
?>
Connecting to MySQL Database
PHP can connect to MySQL to store or get data easily.
Example:
<?php
$conn = new mysqli("localhost", "username", "password", "database");
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
$sql = "SELECT id, name FROM users";
$result = $conn->query($sql);
if ($result->num_rows > 0) {
while($row = $result->fetch_assoc()) {
echo "ID: " . $row["id"]. " - Name: " . $row["name"]. "<br>";
}
} else {
echo "No results found";
}
$conn->close();
?>
Handling File Uploads
PHP can upload files from user computers and save them on your server.
HTML form example:
<form action="upload.php" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
Select file:
<input type="file" name="fileToUpload"><br>
<input type="submit" value="Upload">
</form>
PHP upload code:
<?php
$target_dir = "uploads/";
$target_file = $target_dir . basename($_FILES["fileToUpload"]["name"]);
if (move_uploaded_file($_FILES["fileToUpload"]["tmp_name"], $target_file)) {
echo "File ". htmlspecialchars(basename($_FILES["fileToUpload"]["name"])) . " uploaded successfully.";
} else {
echo "Error uploading your file.";
}
?>
Managing Sessions and Cookies
Sessions and cookies help remember users on your site.
Start a session and set a variable:
<?php
session_start();
$_SESSION["username"] = "JohnDoe";
echo "Session started for " . $_SESSION["username"];
?>
Set a cookie:
<?php
setcookie("user", "JohnDoe", time() + (86400 * 30), "/"); // expires in 30 days
?>++
