- 1. Implement the data link layer framing methods such as character, character stuffing and bit stuffing
- 2. Write a program to compute CRC code for the polynomials CRC-12, CRC-16 and CRC CCIP
- 3. Develop a simple data link layer that performs the flow control using the sliding window protocol, and loss recovery using the Go-Back-N mechanism.
- 5. Take an example subnet of hosts and obtain a broadcast tree for the subnet
- 6. Implement distance vector routing algorithm for obtaining routing tables at each node
- 7. Implement data encryption and data decryption
- 8. Write a program for congestion control using Leaky bucket algorithm
- 9. Write a program for frame sorting technique used in buffers
-
10. Wireshark
i. Packet Capture Using Wire shark
ii. Starting Wire shark
iii. Viewing Captured Traffic
iv. Analysis and Statistics & Filters - 11. How to run Nmap scan
- 12. Operating System Detection using Nmap
-
13. Do the following using NS2 Simulator
i. NS2 Simulator-Introduction
ii. Simulate to Find the Number of Packets Dropped
iii. Simulate to Find the Number of Packets Dropped by TCP/UDP
iv. Simulate to Find the Number of Packets Dropped due to Congestion
v. Simulate to Compare Data Rate& Throughput.
vi. Simulate to Plot Congestion for Different Source/Destination
vii. Simulate to Determine the Performance with respect to Transmission of Packets
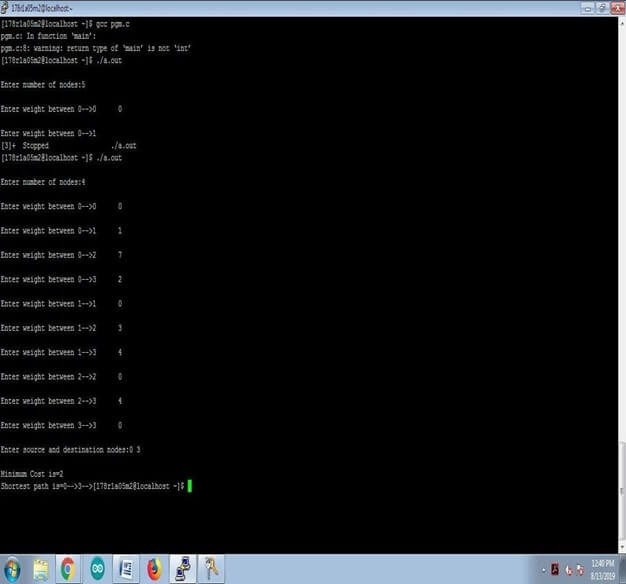
Aim: write a c-program for implement the dijikstra’s Algorithm.
Dijikstra’s Algorithm (Theory):
Dijkstra’s Algorithm allows you to calculate the shortest path between one node (you pick which one) and every other node in the graph. You’ll find a description of the algorithm at the end of this page, but, let’s study the algorithm with an explained example! Let’s calculate the shortest path between node C and the other nodes in our graph: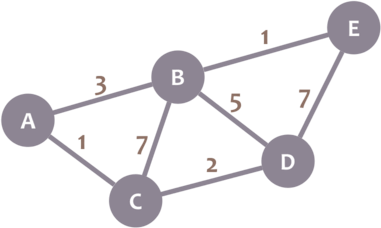
During the algorithm execution, we’ll mark every node with its minimum distance to node C (our selected node). For node C, this distance is 0. For the
rest of nodes, as we still don’t know that minimum distance, it starts being infinity (∞):
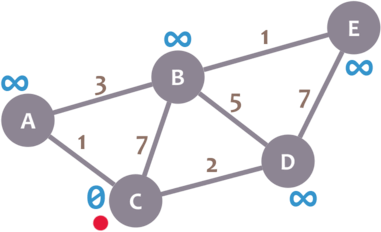
We’ll also have a current node. Initially, we set it to C (our selected node). In the image, we mark the current node with a red dot.
Now, we check the neighbours of our current node (A, B and D) in no specific order. Let’s begin with B. We add the minimum distance of the current node (in this case, 0) with the weight of the edge that connects our current node with B (in this case, 7), and we obtain 0 + 7 = 7. We compare that value with the minimum distance of B (infinity); the lowest value is the one that remains as the minimum distance of B (in this case, 7 is less than infinity):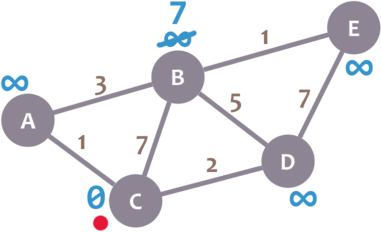
So far, so good. Now, let’s check neighbour A. We add 0 (the minimum distance of C, our current node) with 1 (the weight of the edge connecting our current node with A) to obtain 1. We compare that 1 with the minimum distance of A (infinity), and leave the smallest value: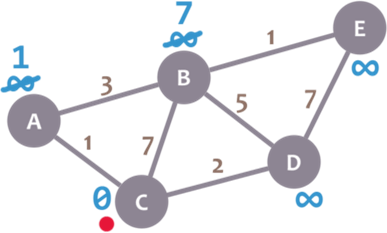
Ok. Repeat the same procedure for D:
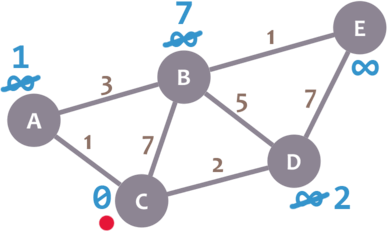
Great. We have checked all the neighbours of C. Because of that, we mark it as visited. Let’s represent visited nodes with a green check mark:
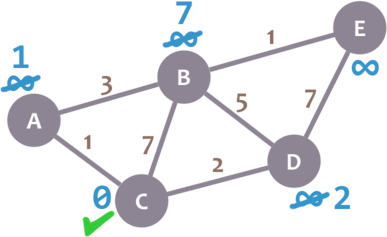
We now need to pick a new current node. That node must be the unvisited node with the smallest minimum distance (so, the node with the smallest number and no check mark). That’s A. Let’s mark it with the red dot:
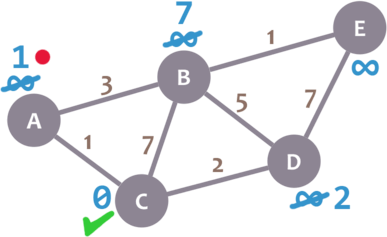
And now we repeat the algorithm. We check the neighbours of our current node, ignoring the visited nodes. This means we only check B.
For B, we add 1 (the minimum distance of A, our current node) with 3 (the weight of the edge connecting A and B) to obtain 4. We compare that 4 with the minimum distance of B (7) and leave the smallest value: 4.
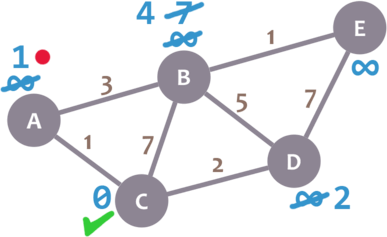
Afterwards, we mark A as visited and pick a new current node: D, which is the non-visited node with the smallest current distance.
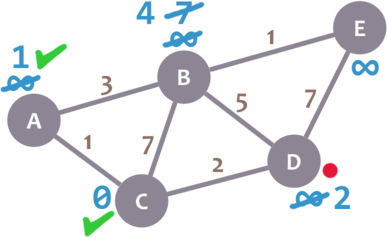
We repeat the algorithm again. This time, we check B and E.
For B, we obtain 2 + 5 = 7. We compare that value with B’s minimum distance (4) and leave the smallest value (4). For E, we obtain 2 + 7 = 9, compare it with the minimum distance of E (infinity) and leave the smallest one (9).
We mark D as visited and set our current node to B.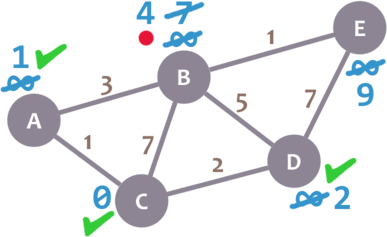
Almost there. We only need to check E. 4 + 1 = 5, which is less than E’s minimum distance (9), so we leave the 5. Then, we mark B as visited and set E as the current node.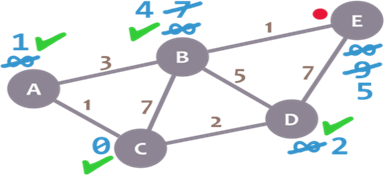
E doesn’t have any non-visited neighbours, so we don’t need to check anything. We mark it as visited.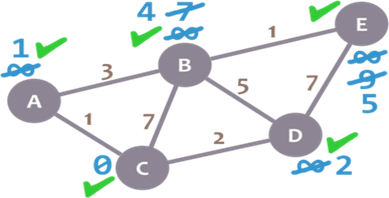
As there are not univisited nodes, we’re done! The minimum distance of each node now actually represents the minimum distance from that node to node C (the node we picked as our initial node)!
Here’s a description of the algorithm:
- Mark your selected initial node with a current distance of 0 and the rest with
- Set the non-visited node with the smallest current distance as the current node C.
- For each neighbour N of your current node C: add the current distance of C with the weight of the edge connecting C-N. If it’s smaller than the current distance of N, set it as the new current distance of N.
- Mark the current node C as
- If there are non-visited nodes, go to step
program:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
//#include<string.h>
#define M_NODES 10
#define INFINITY 1000
int n,dis[M_NODES][M_NODES];
void main()
{
void spath(int,int);
int i,j,g[100][100],s,t,c;
printf(“\nEnter number of nodes:”);
scanf(“%d”,&n);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=i;j<n;j++)
{
printf(“\nEnter weight between
%d– >%d\t”,i,j);
scanf(“%d”,&c);
if(c>=0)
dis[i][j]=c;
else
}
}
exit(0);
printf(“\nEnter source and destination
nodes:”);
scanf(“%d%d”,&t,&s);
spath(s,t);
//getch();
}
void spath(int s,int t)
{
struct state
{
int pre,len;
enum{permanet,tentative} label;
}
state[M_NODES];
int i,k,min,path[20],c=0;
struct state *p;
for(p=&state[0];
p<&state[n];p++)
{
p->pre=-1;
p->len=INFINITY;
p->label=tentative;
}
state[t].len=0;
state[t].label=permanet;
k=t;
do
{
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
if(dis[k][i]!=0&&state[i].label==tentative)
{
if(state[k].len+dis[k][i]<state[i].len)
{
}
}
k=0;
state[i].pre=k;
state[i].len=state[k].len+dis[k][i];
min=INFINITY;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(state[i].label==tentative&&state[i].len<min )
{
min=state[i].len; k=i;
}
}
state[k].label=permanet;
}
while(k!=s); i=0;
k=s; do
{
path[i++]=k; k=state[k].pre; c++;
}
while(k>=0);
printf(“\nMinimum Cost is=%d”,min);
printf(“\nShortest path is=”);
for(k=c-1;k>=0;k–)
printf(“%d–>”,path[k]);
}
Output: