- 4. Implement Dijsktra’s algorithm to compute the shortest path through a network
- 5. Take an example subnet of hosts and obtain a broadcast tree for the subnet
- 6. Implement distance vector routing algorithm for obtaining routing tables at each node
- 7. Implement data encryption and data decryption
- 8. Write a program for congestion control using Leaky bucket algorithm
- 9. Write a program for frame sorting technique used in buffers
-
10. Wireshark
i. Packet Capture Using Wire shark
ii. Starting Wire shark
iii. Viewing Captured Traffic
iv. Analysis and Statistics & Filters - 11. How to run Nmap scan
- 12. Operating System Detection using Nmap
-
13. Do the following using NS2 Simulator
i. NS2 Simulator-Introduction
ii. Simulate to Find the Number of Packets Dropped
iii. Simulate to Find the Number of Packets Dropped by TCP/UDP
iv. Simulate to Find the Number of Packets Dropped due to Congestion
v. Simulate to Compare Data Rate& Throughput.
vi. Simulate to Plot Congestion for Different Source/Destination
vii. Simulate to Determine the Performance with respect to Transmission of Packets
Aim:Develop a simple data link layer that performs the flow control using the sliding window protocol, and loss recovery using the Go-Back-N mechanism.
Sliding Window Protocol :
In computer networks sliding window protocol is a method to transmit data on a network. Sliding window protocol is applied on the Data Link Layer of OSI model. At data link layer data is in the form of frames. In Networking, Window simply means a buffer which has data frames that needs to be transmitted.
Both sender and receiver agrees on some window size. If window size=w then after sending w frames sender waits for the acknowledgement (ack) of the first frame.
As soon as sender receives the acknowledgement of a frame it is replaced by the next frames to be transmitted by the sender. If receiver sends a collective or cumulative acknowledgement to sender then it understands that more than one frames are properly received, for eg:- if ack of frame 3 is received it understands that frame 1 and frame 2 are received properly.
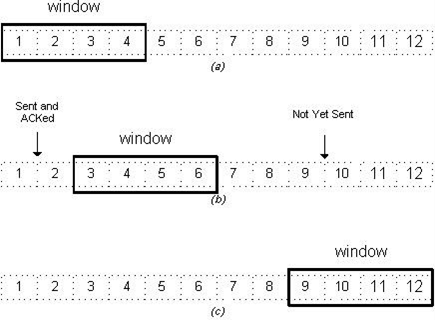
In sliding window protocol the receiver has to have some memory to compensate any loss in transmission or if the frames are received unordered.
Efficiency of Sliding Window Protocol
η = (W*tx)/(tx+2tp)
W = Window Size
tx = Transmission time tp = Propagation delay
Sliding window works in full duplex mode It is of two types:-
- Selective Repeat: Sender transmits only that frame which is erroneous or is lost.
- Go back n: Sender transmits all frames present in the window that occurs after the error bit including error bit
Program:
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int w,i,f,frames[50];
printf(“Enter window size: “);
scanf(“%d”,&w);
printf(“\nEnter number of frames to transmit: “);
scanf(“%d”,&f);
printf(“\nEnter %d frames: “,f);
for(i=1;i<=f;i++)
scanf(“%d”,&frames[i]);
printf(“\nWith sliding window protocol the frames will be sent in
the following manner (assuming no corruption of frames)\n\n”);
printf(“After sending %d frames at each stage sender waits for
acknowledgement sent by the receiver\n\n”,w);
for(i=1;i<=f;i++)
{
if(i%w==0)
{
printf(“%d\n”,frames[i]);
printf(“Acknowledgement of above frames sent is received by
sender\n\n”);
}
else
printf(“%d “,frames[i]);
}
if(f%w!=0)
printf(“\nAcknowledgement of above frames sent is received by
sender\n”);
return 0;
}
Output:
Enter window size: 3
Enter number of frames to transmit: 5
Enter 5 frames: 12 5 89 4 6
With sliding window protocol the frames will be sent in the following manner (assuming no corruption of frames)
After sending 3 frames at each stage sender waits for acknowledgement sent by the receiver 12 5 89
Acknowledgement of above frames sent is received by sender 4 6
Acknowledgement of above frames sent is received by sender
