Example Data Link Protocols
In the context of data link protocols, two prominent examples are the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) used over SONET (Synchronous Optical Networking) and ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Loop) links. These protocols facilitate the transmission of packets over point-to-point connections, which are essential for wide-area networks (WANs) and connecting end-users to the Internet.
1. Packet over SONET
SONET is a widely adopted physical layer protocol that operates over optical fiber links, providing high-speed data transmission, such as 2.4 Gbps for an OC-48 link. To effectively transport packets over SONET, a framing mechanism is necessary to differentiate between the continuous bitstream and the discrete packets being sent. This is where PPP comes into play.
Key Features of PPP:
→ Framing Method: PPP delineates frames using a specific format that includes a start flag, address, control, protocol, payload, and checksum. The start flag (0x7E) indicates the beginning and end of a frame, while byte stuffing is used to prevent confusion with the flag byte within the payload.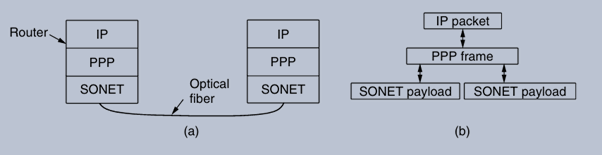
Packet over SONET (a) A protocol stack. (b) Frame relationships
→ Link Control Protocol (LCP): LCP is responsible for establishing, configuring, and testing the link. It negotiates options and can bring the link down gracefully when no longer needed.
→ Network Control Protocols (NCP): PPP supports multiple network layer protocols through NCPs, allowing for the negotiation of options independent of the specific network layer protocol in use.
The PPP frame format closely resembles HDLC (High-level Data Link Control), with the primary distinction being that PPP is byte-oriented, while HDLC is bit-oriented. This design choice simplifies the implementation of error detection and framing.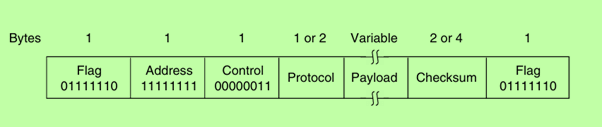
Link Establishment Phases: The PPP link goes through several states during its lifecycle:
DEAD: No physical connection exists.
ESTABLISH: A physical connection is established, and LCP packets are exchanged to negotiate options.
→ AUTHENTICATE: If authentication is required, the peers verify each other’s identities.
→ NETWORK: NCP packets are exchanged to configure the network layer.
→ OPEN: Data transport occurs in this state.
→ TERMINATE: The link is taken down, returning to the DEAD state.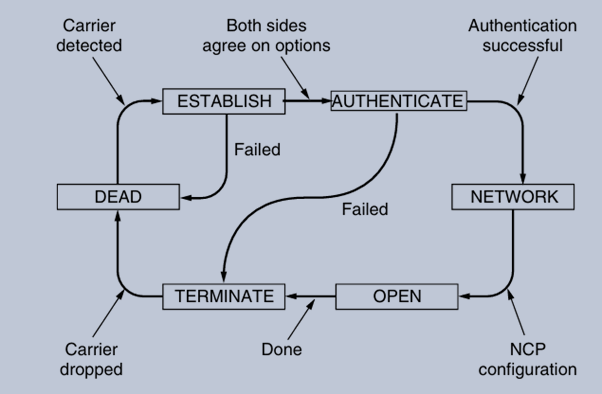
State diagram for bringing a PPP link up and down.
2. ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Loop)
ADSL technology connects millions of users to the Internet over existing telephone lines, enabling high-speed data transmission. The ADSL architecture includes a DSL modem at the user’s end and a DSLAM (DSL Access Multiplexer) at the service provider’s end.
Protocol Stack for ADSL:
→ Physical Layer: ADSL employs a modulation technique known as orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM).
→ PPP: Similar to its use over SONET, PPP is utilized to establish the link and carry IP packets over the ADSL connection.
→ ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode): ADSL uses ATM for data transmission, which operates with fixed-length cells (53 bytes) and is connection-oriented, allowing for efficient bandwidth management.
→ AAL5 (ATM Adaptation Layer 5): AAL5 is used to adapt packet data into ATM cells, providing a trailer for error detection and length information.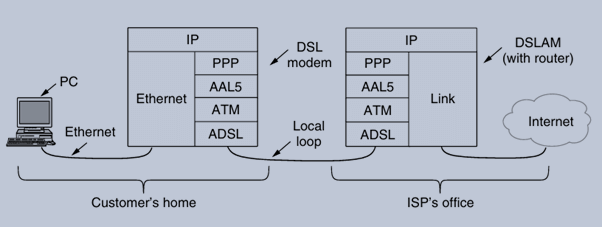
ADSL protocol stacks
PPPoA (PPP over ATM):
PPPoA is a specification that outlines how PPP frames are encapsulated within AAL5 frames for transmission over ATM. In this setup:
→ The PPP protocol and payload are placed directly into the AAL5 payload.
→ The ATM virtual circuit identifier ensures that the cells are routed correctly.
→ Framing and CRC from PPP are not needed, as AAL5 already provides these functionalities. 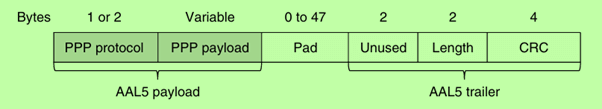
Conclusion
Both PPP over SONET and ADSL illustrate the versatility of data link protocols in facilitating reliable communication over various physical layers. By employing framing mechanisms, error detection, and link control protocols, these technologies enable efficient data transmission across wide-area networks and local loops, connecting users to the Internet seamlessly.
