Fiber-Optic Cable
A fiber-optic cable is made of glass or plastic and transmits signals in the form of light. Light travels in a straight line as long as it is moving through a single uniform substance.
If a ray of light traveling through one substance suddenly enters another substance(of a different density), the ray changes direction.
Bending of light ray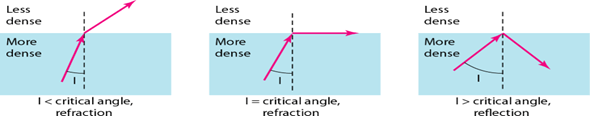
Optical fibers use reflection to guide light through a channel. A glass or plastic core is surrounded by a cladding of less dense glass or plastic.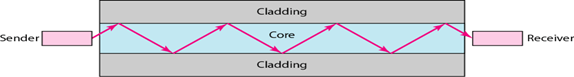
Propagation Modes
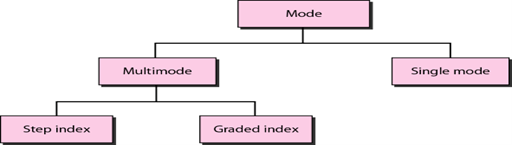 Multimode is so named because multiple beams from a light source move through the core in different paths. How these beams move within the cable depends on the structure of the core, as shown in Figure
Multimode is so named because multiple beams from a light source move through the core in different paths. How these beams move within the cable depends on the structure of the core, as shown in Figure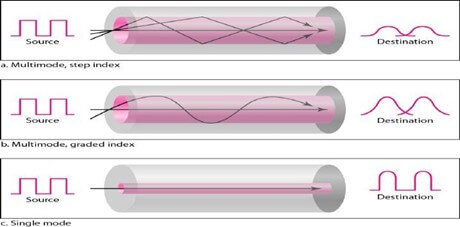
In multimode step-index fiber, the density of the core remains constant from the center to the edges. A beam of light moves through this constant density in a straight line until it reaches the interface of the core and the cladding. The term step index refers to the suddenness of this change, which contributes to the distortion of the signal as it passes through the fiber.
A second type of fiber, called multimode graded-index fiber, decreases this distortion of the signal through the cable. The word index here refers to the index of refraction.
Single-Mode: Single-mode uses step-index fiber and a highly focused source of light that limits beams to a small range of angles, all close to the horizontal
Fiber Construction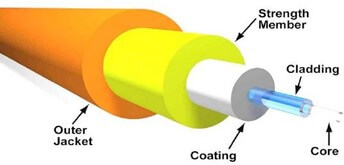
The subscriber channel (SC) connector, The straight-tip (ST) connector, MT-RJ(mechanical transfer registered jack) is a connector
Applications
Fiber-optic cable is often found is backbone networks because its wide bandwidth cost-effective..
Some cable TV companies use a combination of optical fiber and coaxial cable, thus creating a hybrid network.
Local-area networks such as 100Base-FX network (Fast Ethernet) and 1000Base-X also use fiber-optic cable.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Optical Fiber
Advantages: Fiber-optic cable has several advantages over metallic cable (twisted pair or coaxial).
→ Higher Bandwidth.
→ Less signal attenuation. Fiber-optic transmission distance is significantly greater than that of other guided media. A signal can run for 50 km without requiring regeneration. We need repeaters every 5 km for coaxial or twisted- pair
→ Immunity to electromagnetic interference. Electromagnetic noise cannot affect fiber-optic
→ Resistance to corrosive materials. Glass is more resistant to corrosive materials than
→ Light weight. Fiber-optic cables are much lighter than copper
→ Greater immunity to tapping. Fiber-optic cables are more immune to tapping than copper cables. Copper cables create antenna effects that can easily be tapped.
Disadvantages: There are some disadvantages in the use of optical fiber.
→ Installation and maintenance
→ Unidirectional light propagation. Propagation of light is unidirectional. If we need bidirectional communication, two fibers are
→ The cable and the interfaces are relatively more expensive than those of other guided media. If the demand for bandwidth is not high, often the use of optical fiber cannot be justified.
