Coaxial Cable
Coaxial cable (or coax) carries signals of higher frequency ranges than those in twisted pair cable. coax has a central core conductor of solid or stranded wire (usually copper) enclosed in an insulating sheath, which is, in turn, encased in an outer conductor of metal foil, braid, or a combination of the two. The outer metallic wrapping serves both as a shield against noise and as the second conductor, which completes the circuit. This outer conductor is also enclosed in an insulating sheath, and the whole cable is protected by a plastic cover.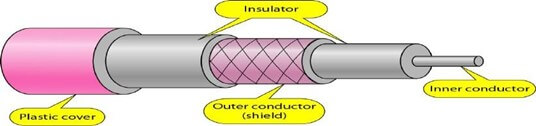
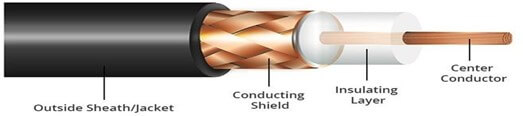
The most common type of connector used today is the Bayone-Neill-Concelman (BNe), connector.
Applications
Coaxial cable was widely used in analog telephone networks, digital telephone networks
Cable TV networks also use coaxial cables.
Another common application of coaxial cable is in traditional Ethernet LANs
