Preparation of Final Accounts
In every business, the business man is interested in knowing whether the business has resulted in profit or loss and what the financial position of the business is at a given time. In brief, he wants to know (i)The profitability of the business and (ii) The soundness of the business.
The trader can ascertain this by preparing the final accounts. The final accounts are prepared from the trial balance. Hence the trial balance is said to be the link between the ledger accounts and the final accounts. The final accounts of a firm can be divided into two stages. The first stage is preparing the trading and profit and loss account and the second stage is preparing the balance sheet.
Trading Account
The first step in the preparation of final account is the preparation of trading account. The main purpose of preparing the trading account is to ascertain gross profit or gross loss as a result of buying and selling the goods.
Finally, a ledger may be defined as a summary statement of all the transactions relating to a person, asset, expense or income which have taken place during a given period of time. The up-to-date state of any account can be easily known by referring to the ledger.
Profit and Loss Account
The business man is always interested in knowing his net income or net profit. Net profit represents the excess of gross profit plus the other revenue incomes over administrative, sales, financial and other expenses. The debit side of profit and loss account shows the expenses and the credit side the incomes. If the total of the credit side is more, it will be the net profit. And if the debit side is more, it will be net loss.
Format of Trading and Profit & Loss A/C of ……….for the year ending ……………..
| Particulars | Amount | Particulars | Amount |
| To Opening stock | xxxx | By Sales | xxxx |
| To Purchases | xxxx | Less: Returns | xxxx |
| Less: Returns | xxxx | By Closing stock | xxxx |
| To Carriage inwards | xxxx | By Gross loss (c/d) | xxxx |
| To Freight, cartage | xxxx | ||
| To Customs duty | xxxx | ||
| To Clearing charges | xxxx | ||
| To Octroi | xxxx | ||
| To Wages | xxxx | ||
| To Gas, water, coal, light | xxxx | ||
| To Factory rent | xxxx | ||
| To Works manager salary | xxxx | ||
| To Factory supervision | xxxx | ||
| To consumable stores | xxxx | ||
| To Plant depreciation | xxxx | ||
| To Gross profit (c/d) | xxxx | ||
| xxxx | xxxx | ||
| To Gross loss (b/d) | xxxx | By Gross profit (b/d) | xxxx |
| To Salaries | xxxx | By Discount received | xxxx |
| To Rent, Taxes | xxxx | By Interest received | xxxx |
| To Insurance | xxxx | By Dividend received | xxxx |
| To Printing stationery | xxxx | By Rent received | xxxx |
| To Advertisement | xxxx | By Commission received | xxxx |
| To Carriage outward | xxxx | By Net loss (c/d) | xxxx |
| To Bad debts | xxxx | xxxx | |
| To Repairs | xxxx | xxxx | |
| To Depreciation | xxxx | xxxx | |
| To Discount allowed | xxxx | xxxx | |
| To Commission allowed | xxxx | xxxx | |
| To Interest paid | xxxx | xxxx | |
| To Provision for doubtful debts | xxxx | xxxx | |
| To Postage | xxxx | xxxx | |
| To General expenses | xxxx | xxxx | |
| To Net profit (c/d) | xxxx | xxxx | |
| xxxx | xxxx |
Balance Sheet
The second point of final accounts is the preparation of balance sheet. It is prepared often in the trading and profit, loss accounts have been compiled and closed. A balance sheet may be considered as a statement of the financial position of the concern at a given date.
A balance sheet is an item wise list of assets, liabilities and proprietorship of a business at a certain state.
Balance Sheet of……………….company as on ……………..
| Capital & Liabilities | Amount | Assets | Amount |
| Capital | xxxx | Land and buildings | xxxx |
| Add: Net profit | xxxx | Furniture | xxxx |
| xxxx | Plant and machinery | xxxx | |
| Less: Drawings | xxxx | Land | xxxx |
| Loans | xxxx | Vehicles | xxxx |
| Bank Over Draft | xxxx | Debtors | xxxx |
| Bills payable | xxxx | Investments | xxxx |
| Creditors | xxxx | Bills receivables | xxxx |
| Outstanding expenses | xxxx | Goodwill | xxxx |
| Incomes received in advance | xxxx | Patents | xxxx |
| All reserves | xxxx | Copyright | xxxx |
| Trade marks | xxxx | ||
| Prepaid expenses | xxxx | ||
| Incomes receivables | xxxx | ||
| Securities | xxxx | ||
| Closing stock | xxxx | ||
| Cash in hand | xxxx | ||
| Cash at bank | xxxx | ||
| xxxx | xxxx |
Final Accounts Preparation
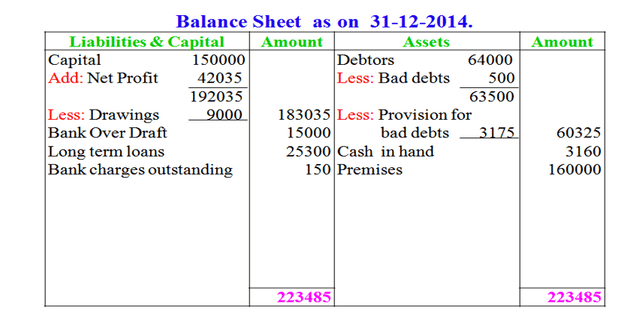
Example: From the following trial balance and additional information, prepare final accounts for the year ending 31-12-2014.
Trial Balance
| Particulars | Rs | Particulars | Rs |
| Sundry debtors | 64,000 | Discount received | 9,000 |
| Stock (1-1-2014) | 44,000 | Bank over draft | 15,000 |
| Cash in hand | 3,160 | Long term loan | 25,300 |
| Wages | 35,000 | Sales | 3,65,000 |
| Trade expenses | 2,150 | Capital | 1,50,000 |
| Gas, water, power | 4,450 | ||
| Sales returns | 800 | ||
| Bank charges | 1,800 | ||
| Purchases | 2,37,740 | ||
| Advertisements | 2,200 | ||
| Premises | 1,60,000 | ||
| Drawings | 9,000 | ||
| 5,64,300 | 5,64,300 |
Adjustments
1. Bank charges outstanding Rs.150
2. Write off bad debts Rs. 500
3. Provide 5% for doubtful debts

Example:From the following data prepare final accounts for the year ending 31-12-2014.
Trial Balance
| Particulars | Rs | Rs |
| Drawings and capital | 12,000 | 80,000 |
| Opening stock | 12,000 | |
| Investments | 30,600 | |
| Stationery | 12,000 | |
| Carriage | 3,000 | |
| Returns | 6,000 | 2,600 |
| Purchases and sales | 1,20,000 | 1,60,000 |
| Loans | 2,400 | 10,000 |
| Debtors and creditors | 60,000 | 25,000 |
| Discount allowed | 2,200 | |
| Freight in | 10,400 | |
| Freight out | 6,000 | |
| Charity | 28,000 | |
| Reserve for doubtful debts | 2,000 | |
| Bills payables | 25,000 | |
| Total | 3,04,600 | 3,04,600 |
Adjustments
1. Closing stock Rs. 20,000
2. Appreciate investment by 10%
3. Maintain reserve for doubtful debts at the rate of 5%
4. Provide 5% as interest on capital


