Double Entry System of Accounting
The double entry system of accounting is a foundational concept in the field of financial accounting and bookkeeping. This system is predicated on the principle that every financial transaction affects at least two accounts, ensuring that the accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Equity) remains balanced. The double entry system provides a comprehensive method for recording financial transactions, which enhances accuracy and accountability in financial reporting.
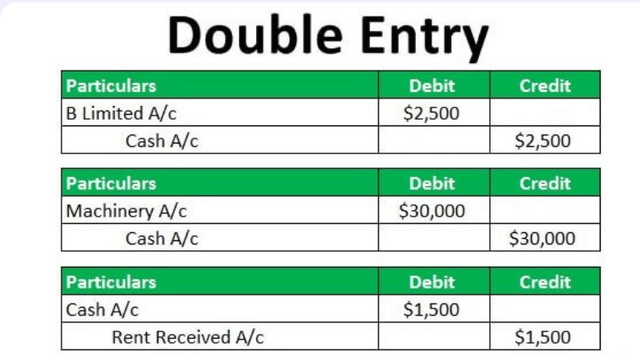
Key Features of the Double Entry System
Dual Aspect: Each transaction has dual effects; for example, if a business purchases inventory with cash, it increases the inventory account while simultaneously decreasing the cash account. This dual aspect ensures that all entries are recorded in a manner that reflects their impact on both sides of the accounting equation.
Debits and Credits: In this system, every transaction is recorded as both a debit and a credit. Debits must equal credits for each transaction, maintaining balance within the ledger. For instance, when a company sells goods for cash, it would record an increase in cash (debit) and an increase in sales revenue (credit).
Account Types: The double entry system categorizes accounts into five main types: assets, liabilities, equity, revenues, and expenses. Each type has its own rules regarding how debits and credits affect them:
- Assets: Increased by debits and decreased by credits.
- Liabilities: Increased by credits and decreased by debits.
- Equity: Similar to liabilities; increased by credits.
- Revenues: Increased by credits.
- Expenses: Increased by debits.
Trial Balance: At any point in time, businesses can prepare a trial balance to verify that total debits equal total credits across all accounts. This serves as an internal control mechanism to detect errors in recording transactions.
Financial Statements Preparation: The double entry system facilitates the preparation of key financial statements such as the balance sheet and income statement. These statements provide stakeholders with insights into the company’s financial health.
Historical Significance: The origins of double entry bookkeeping can be traced back to 15th-century Italy, notably through the work of Luca Pacioli, who is often referred to as the “father of accounting.” His seminal work laid down principles that are still relevant today.
Advantages Over Single Entry System
- Enhanced accuracy due to checks and balances inherent in recording both sides of transactions.
- Better fraud detection capabilities since discrepancies are more easily identified.
- Comprehensive tracking of financial performance over time.
Software Integration: Modern accounting software utilizes double entry principles to automate many aspects of bookkeeping, making it easier for businesses to maintain accurate records without extensive manual effort.
Conclusion
The double entry system is essential for effective financial management within organizations. It not only ensures accuracy but also provides valuable insights into business operations through systematic record-keeping practices.
