- Declaring Variables in PHP
- PHP Data Types
- PHP Arrays
- Types of PHP Operators
- PHP Strings
- PHP Expressions
- PHP Control Structures
- PHP Functions
- PHP Form Handling – Read Form Inputs & Handle File Uploads
- How to Connect PHP to MySQL Database Using MySQLi
- Executing Simple Queries in PHP
- Handling Results in PHP
- Handling Sessions and Cookies
PHP Form Handling:
Reading Data from Web Form Controls and File Uploads
Reading Data from Text Boxes, Radio Buttons, Lists, etc.
PHP allows reading data from web form controls using superglobal arrays like $_GET and $_POST. These controls include:
Text boxes
Radio buttons
Checkboxes
Select lists (dropdowns)
Text areas
When a user submits a form, the data is sent to the server for processing. This is done using either the GET or POST method.
Example: HTML Form Using POST
<form action="welcome.php" method="post">
Name: <input type="text" name="name"><br>
E-mail: <input type="text" name="email"><br>
<input type="submit">
</form>
Example: PHP Script (welcome.php)
Welcome <?php echo $_POST["name"]; ?><br>
Your email address is: <?php echo $_POST["email"]; ?>
If the method is set to GET, use $_GET["name"] and $_GET["email"] instead.
GET vs POST
GET:
Appends data in the URL
Data is visible
Limited to ~2000 characters
Can be bookmarked
Not secure for sensitive information
POST:
Sends data in HTTP body
Not visible in URL
No data limit
Suitable for sensitive and large data
Required for file uploads
Accessing Form Data in PHP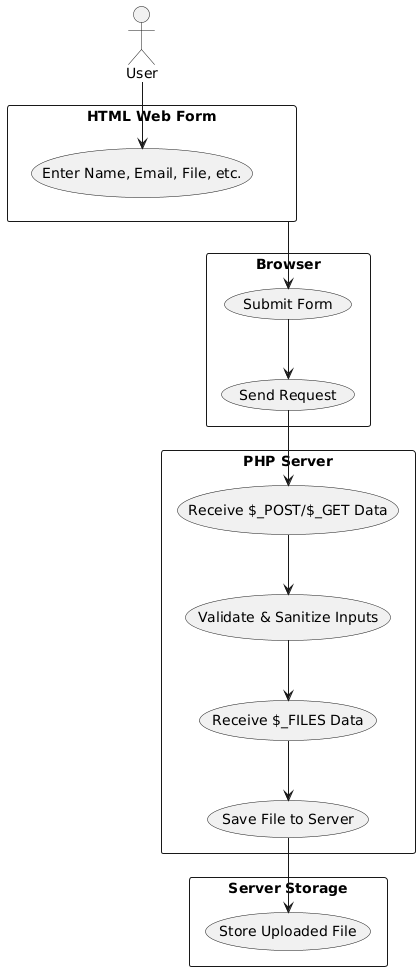
Example: Reading Form Values
if ($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST") {
$name = $_POST['name'];
$gender = $_POST['gender'];
$hobbies = $_POST['hobbies'];
$country = $_POST['country'];
}
Validating and Sanitizing Form Inputs
To protect from security issues like SQL injection or XSS, always validate user input.
Example: Basic Validation
$name = trim($_POST['name']);
if (!empty($name)) {
$name = htmlspecialchars($name);
} else {
echo "Name is required.";
}
Handling File Uploads in PHP
PHP supports file uploads using the $_FILES superglobal. You must set the form’s enctype to multipart/form-data.
Example: HTML Form for File Upload
<form action="upload.php" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
Select file: <input type="file" name="myFile"><br>
<input type="submit" value="Upload">
</form>
Example: PHP Script (upload.php)
if ($_FILES["myFile"]["error"] == 0) {
move_uploaded_file($_FILES["myFile"]["tmp_name"], "uploads/" . $_FILES["myFile"]["name"]);
echo "File uploaded successfully.";
} else {
echo "File upload error.";
}
Key Points for File Uploads:
Always check for upload errors.
Validate file type and size.
Use
move_uploaded_file()to store the file safely.Set proper file permissions on the server.
Conclusion
Reading data from form controls and handling file uploads are essential in PHP web applications. Use POST for secure data handling and always validate user input. With careful processing, you can create powerful, user-friendly, and secure web forms.
